Metal stamping is a manufacturing process that transforms flat metal sheets into functional components. If you don’t select proper materials, you won’t be able to achieve the desired outcome. If you are looking to get technical insights, consider reading the whole article.
What is metal stamping?
Metal stamping is a cold-forming process that uses a die and a punch to cut, bend, and shape sheet metal into various forms and sizes. Metal stamping and fabrication is often used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
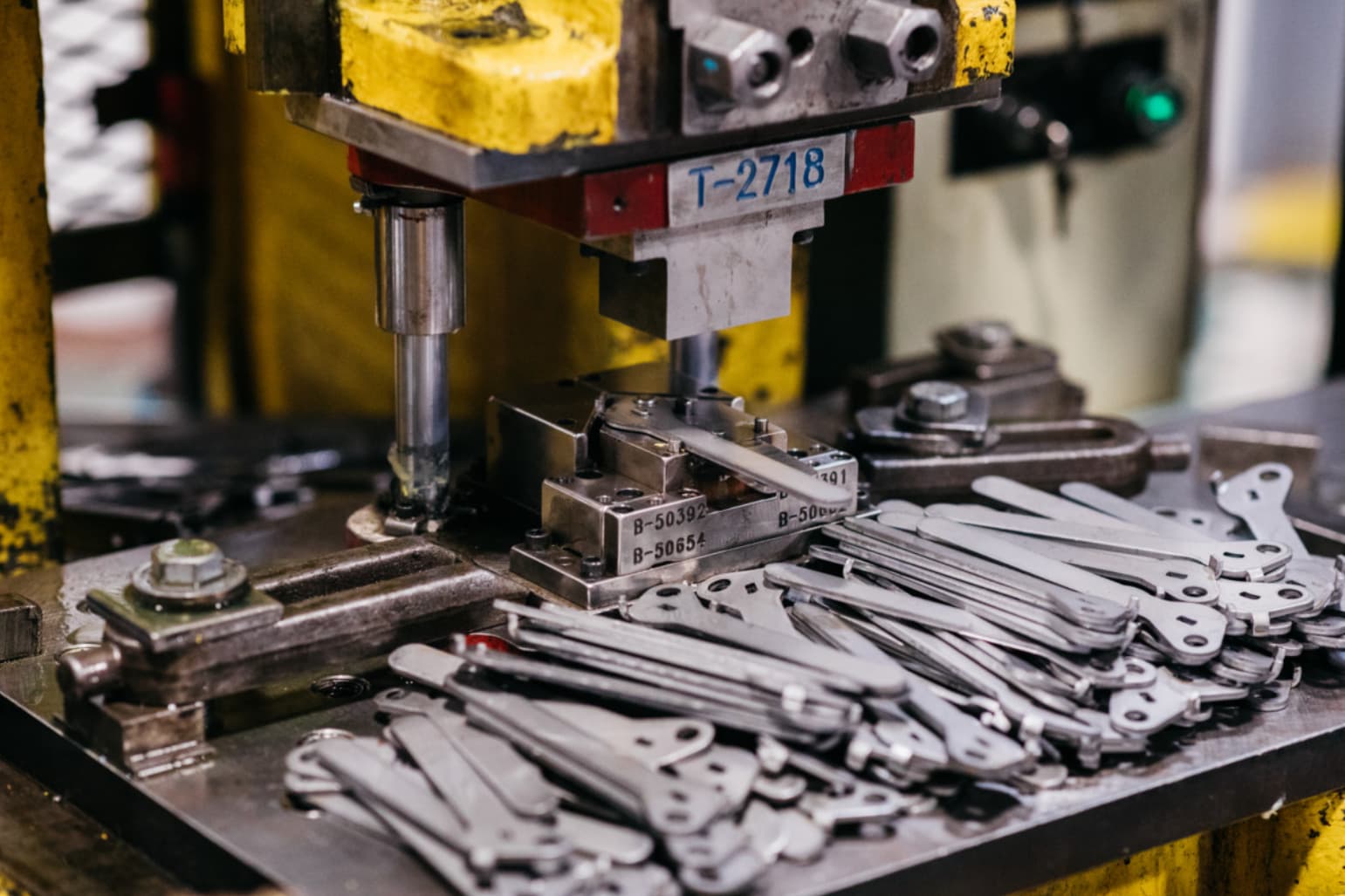

The process of metal stamping is to place metal sheets between the die and the punch and then apply pressure to deform the metal and create the desired shape. Mechanical presses, hydraulic presses, and servo presses are used for metal stamping.
Application, cost, bend rating, finishing options, and tensile strength are the main factors when choosing material for metal Stamping. Copper, steel, stainless steel, brass, beryllium copper, and aluminum are commonly used. These materials offer corrosion resistance, decorative appeal, flexibility, and easy sanitization.
Importance of selecting the right materials for metal stamping
Here are some ideas from JCLDD sheet metal fabrication manufacturer about deep draw manufacturing.
While doing sheet metal material selection, don’t forget to consider some key factors. This will ensure the success of the process and the production of high-quality, precise stamped parts.
Cost: Different materials have different costs and choosing the wrong one can significantly impact the project budget. Steel and aluminum alloys are Cost-effective options
Product Use: The material will directly affect the final product's durability, functionality, and performance. Select a material that can withstand your expected demands and environmental conditions.
Durability: Select materials that can withstand the stamping process. Using the wrong materials won’t make products durable or long-lasting. Consider factors such as strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
Functionality: The material you choose will determine how well the part performs its intended function. Consider properties such as electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and magnetic permeability, depending on the specific application.
Design Requirements: Some materials are more difficult to work with than others. Choose a material that can be easily formed into the desired shape and integrated with other components, considering factors like formability, weldability, and machinability.
Selecting the right materials is important to succeed in the metal stamping process. It directly impacts the final product's quality, durability, functionality, and cost-effectiveness.
Overview of Materials Used in Metal Stamping
There are several types of materials used in metal stamping. These materials have different characteristics and properties that make them suitable for specific applications. Understanding the properties of each material is important in selecting the right one for your metal stamping project.
Common Types of Materials Used in Metal Stamping
A variety of materials are commonly used in metal stamping and industrial metal stamping, to create intricate and precise parts for various applications. These materials can be broadly classified into two categories: ferrous and non-ferrous.
Ferrous Materials
Carbon Steel: The most widely used material in metal stamping, carbon steel is available in various grades, with low-carbon steel being soft and formable, while high-carbon steel is strong but difficult to form.
Stainless Steel: stainless steel deep drawing manufacturing contains chromium and has different grades with many corrosion resistance and strength levels. It is used for parts that require high strength and corrosion resistance.
Galvanized Steel: Galvanized steel is carbon steel coated with a layer of zinc for added corrosion resistance. It is often used for parts that will be exposed to harsh environments.
Non-Ferrous Materials
Copper: Copper deep drawing is highly conductive with excellent corrosion resistance. It is often used for electrical components and parts that require high conductivity.
Brass: Brass metal stamping is a combination of copper and zinc and has a bright gold-like appearance. It is often used for decorative parts and parts that require good corrosion resistance.
Aluminum: Aluminium deep drawing is lightweight, strong, and has excellent corrosion resistance. It is often used for parts that require a combination of strength, weight savings, and corrosion resistance.
Characteristics and Properties of Materials
You can find a list of the most used Materials for Metal Stamping and their properties below.
Copper:
Steel:
Stainless Steel:
Brass:
Beryllium Copper:
High electrical conductivity
High strength and hardness
Excellent corrosion resistance
Good thermal conductivity
Aluminum:
Factors to Consider When Choosing Materials for Metal Stamping
When choosing materials for metal stamping, there are several factors to consider.
Mechanical Properties
When choosing materials for metal stamping, it's important to consider their mechanical properties, such as strength and flexibility. Strength means the material's ability to resist bending or breaking under force. Flexibility refers to how easily the material can be bent or shaped without breaking.
These properties are important because metal stamping involves using specialized tools and machinery to shape and form metal sheets or coils.
The material needs to be strong enough to withstand the stamping process without getting permanently deformed or damaged.
It also needs to be flexible enough to be easily formed into the desired shape without cracking or breaking.
Imagine you're making a metal bracket for a shelf. You want to use a material that's strong enough to support the weight of the shelf. You also want the material to be flexible enough to bend into the desired shape without breaking.
A material like steel would be a good choice because it's both strong and flexible. Steel is strong enough to support the weight of the shelf and whatever you put on it. It's also flexible enough to be bent into the desired shape without breaking.
Compatibility with the stamping process
When it comes to metal stamping, choosing the right materials is key to a successful project. Here are some things to keep in mind:
Formability: Can the material be bent and shaped without cracking or tearing?
Thickness: Is the material thick enough to handle the stamping process without getting damaged?
Springback: Will the material bounce back to its original shape after being stamped?
Metal surface treatment: Is the material smooth enough to ensure good contact with the stamping tools?
Compatibility with tooling: Does the material work well with the tools and equipment you're using?
Imagine you're making a metal bracelet. You want to use a material that's flexible enough to bend into a circle, but strong enough to hold its shape. You also want the material to have a smooth surface so that the stamping doesn't leave any marks.
By considering these factors, you might choose a material like aluminum or stainless steel. These materials are both formable and strong, and they have a smooth surface finish.
Cost considerations
When choosing a material for metal stamping, it's important to consider the cost. Here are some things you should keep in mind:
1. Initial cost: How much does the material cost per pound or sheet?
2. Scrap rate: How much material is wasted during the stamping process?
3. Tooling costs: Does the material require specialized tooling or equipment?
4. Processing costs: Are there any additional costs associated with processing the material, such as heat treatment or coating?
Some materials may have a higher initial cost, but they may also have a lower scrap rate or require less specialized tooling. This can lead to long-term cost savings.
Environmental and regulatory factors
When choosing a material for metal stamping, it's important to consider environmental and regulatory factors. Here are some things to keep in mind:
Environmental impact: Choose recyclable materials, that have low energy consumption during production, and minimize waste generation.
Regulatory compliance: Ensure that the chosen material complies with relevant regulations and standards. This includes restrictions on hazardous substances, emissions, and worker safety.
Health and safety: Evaluate the potential health and safety risks associated with the material, including toxicity, flammability, and handling requirements.
Waste management: Assess the ease of disposal and recycling of the material to minimize environmental impact and comply with waste management regulations.
Supply chain transparency: Consider the transparency and ethical practices of the material's supply chain to ensure responsible sourcing and minimize social and environmental risks.
Materials for Different Stamping Applications
When considering materials for different stamping applications, it's important to consider the specific requirements of stamping industries.
Materials suitable for automotive stamping
Automotive stamping and automotive metal stamping parts require materials that possess high strength, excellent formability, and superior corrosion resistance. When selecting materials for automotive stamping, consider the following factors:
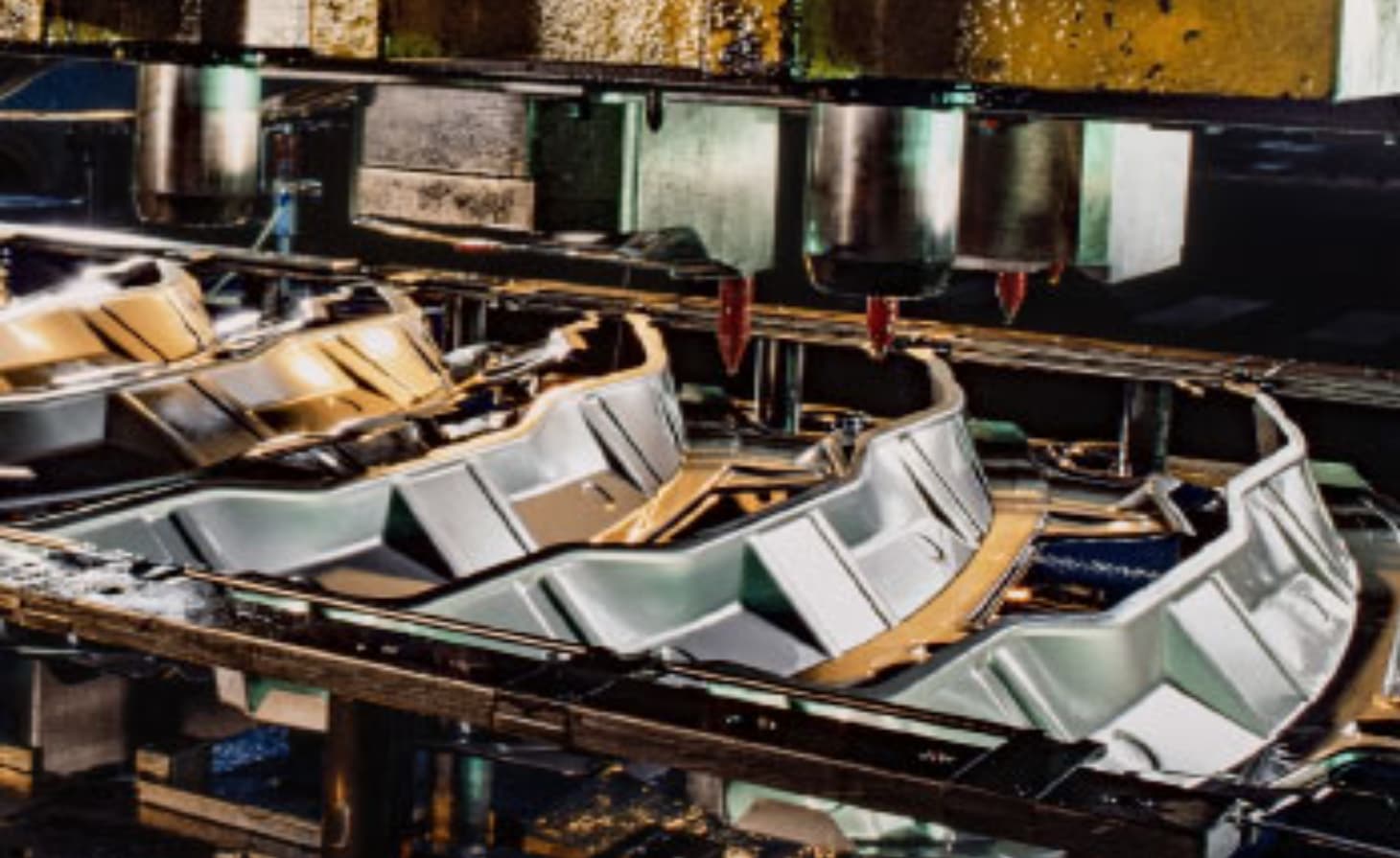

High tensile strength: Choose materials that can withstand mechanical stresses and provide structural integrity to automotive components.
Superior formability: Opt for materials that can be easily shaped and molded into complex geometries without cracking or tearing.
Excellent corrosion resistance: Select materials that can withstand exposure to harsh environmental conditions, such as salt, moisture, and chemicals.
Lightweight properties: Consider materials that are lightweight to improve fuel efficiency and reduce overall vehicle weight.
Cost-effectiveness: Evaluate the cost of materials to ensure they fit within the project's budget while still meeting the required specifications.
Materials used in electronics and telecommunications stamping
Choosing the right materials for stamping electronic and telecommunications components is crucial for ensuring product quality and reliability. Here are key factors to consider with common electronic components:
Electrical Conductivity: Choose materials with high electrical conductivity, such as copper alloys (brass and bronze), to ensure efficient signal transmission.
Corrosion Resistance: Select materials that can withstand harsh environments and chemicals, such as stainless steel, to prevent signal degradation.
Durability: Opt for materials that can withstand repeated mating cycles and mechanical stress, such as copper alloys and stainless steel.
Weight Considerations: Consider lightweight materials, such as aluminum alloys, to reduce the weight of electronic devices.
Cost-effectiveness: Evaluate the cost of materials to ensure they fit within the project's budget.
Materials for medical device stamping
When choosing materials for medical metal stamping, consider these key factors:
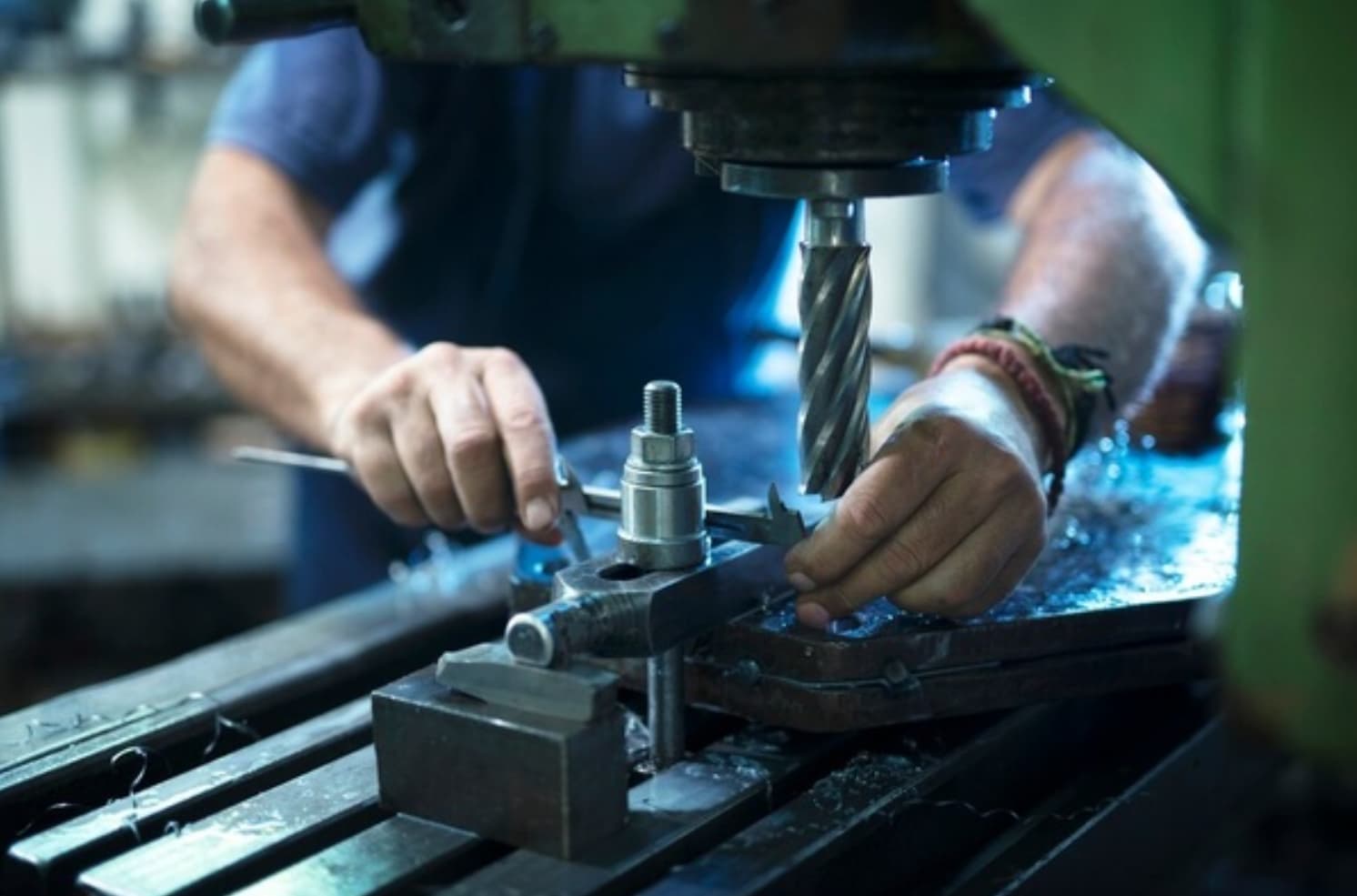

Biocompatibility: Choose materials that are compatible with the human body and won't cause adverse reactions, such as surgical-grade stainless steel and titanium alloys.
Sterilization Suitability: Select materials that can withstand sterilization methods like heat, radiation, or chemicals without compromising their integrity, such as stainless steel.
Corrosion Resistance: Opt for materials that are resistant to corrosion from bodily fluids, such as stainless steel, titanium, and certain plastics.
Mechanical Strength: Use materials with sufficient strength to withstand the stresses and strains of medical device usage, such as stainless steel and titanium alloys.
Electrical Conductivity: Ensure that the materials have the necessary electrical conductivity for devices that require electrical components, such as copper alloys and certain plastics.
Comparison of Commonly Used Materials for Metal Stamping
It's important to know the strengths and weaknesses of the materials used for metal stamping.
Strengths and weaknesses of different materials
Each materials have unique strengths and weaknesses that make them different from others. Here are some key points you should know.
Copper: Corrosion resistant, has decorative appeal, is flexible, and easy to sanitize. It also has antimicrobial properties. But it has a low strength-to-weight ratio and pure copper can be expensive.
Cold Rolled Steel: Known for its versatility, excellent formability, and affordability. However, it's heavy and can corrode if not properly maintained.
Stainless Steel: Provides superior corrosion resistance, attractive surface finish options, and magnetism. Although it can be heavy and can be expensive initially.
Brass: Known for its thermal and electrical conductivity, decorative appearance, and versatility. It has a lower strength-to-weight ratio compared to aluminum and steel.
Aluminum: Lightweight, has high thermal and electrical conductivity, good corrosion resistance, and can be formed and shaped easily. However, it has a lower strength-to-weight ratio compared to steel and can be bent or dented easily.
Beryllium Copper: Offers high electrical conductivity, strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature resistance. But it is expensive and has low ductility and formability.
Conclusion
So, if you are still reading, you should already have a comprehensive understanding of the materials used in metal stamping. Don’t forget to compare the strengths and weaknesses of the materials according to your needs. It will help you choose the best materials for your upcoming metal stamping projects.